Dental assistants play a crucial role in modern dentistry‚ ensuring smooth operations and patient care. Their responsibilities span clinical and administrative tasks‚ supporting dentists and enhancing patient outcomes. This makes their role versatile and essential in healthcare settings.
1.1 Overview of Dental Assisting as a Career
Dental assisting is a rewarding and in-demand career in the healthcare sector. It offers a unique blend of clinical and administrative responsibilities‚ making it an attractive option for those who enjoy hands-on patient care and organizational tasks. Dental assistants work in various settings‚ including private practices‚ clinics‚ and hospitals‚ supporting dentists during procedures and ensuring efficient office operations. The role requires strong communication skills‚ attention to detail‚ and the ability to work well under pressure. With proper training and certification‚ dental assistants can significantly impact patient outcomes and contribute to the success of dental teams. This career path also offers flexible scheduling and opportunities for professional growth.
1.2 Key Responsibilities and Duties
Dental assistants perform a variety of essential tasks to support dentists and ensure efficient patient care. Their duties include preparing patients for procedures‚ maintaining infection control protocols‚ and handling dental instruments. They assist during examinations‚ take dental impressions‚ and process x-rays. Administrative responsibilities involve scheduling appointments‚ managing patient records‚ and handling billing. Effective communication with patients‚ educating them on oral hygiene‚ and providing emotional support are also critical. Dental assistants must stay organized‚ work well under pressure‚ and adhere to safety guidelines. Their role is vital in enhancing patient outcomes and streamlining dental office operations.
Educational Requirements and Training
Completing an accredited dental assistant program is essential. These programs‚ often accredited by the Commission on Dental Accreditation (CODA)‚ combine classroom and clinical training‚ preparing students for professional roles.
2.1 Accredited Dental Assistant Programs
Accredited dental assistant programs are essential for gaining the necessary skills and knowledge. These programs‚ typically lasting 9-11 months‚ combine classroom instruction with hands-on clinical training. They cover topics such as dental terminology‚ anatomy‚ and infection control‚ ensuring students are well-prepared for the profession.
Accreditation by the Commission on Dental Accreditation (CODA) ensures high educational standards. Graduates are eligible to take certification exams‚ such as the Certified Dental Assistant (CDA) exam‚ enhancing their career prospects and compliance with state-specific requirements.
2.2 Importance of On-the-Job Training
On-the-job training is crucial for dental assistants to gain practical experience in real-world settings. It allows them to apply theoretical knowledge and develop hands-on skills‚ such as patient preparation and equipment handling‚ under the supervision of experienced professionals. This training helps assistants adapt to specific dental practices and procedures‚ ensuring they can efficiently support dentists and hygienists. Additionally‚ it fosters teamwork and communication skills‚ which are vital for a smooth workflow in a dental office. On-the-job training also provides opportunities to learn office-specific protocols and software‚ enhancing overall competence and job readiness.
This practical experience is often where assistants refine their ability to interact with patients‚ manage records‚ and maintain infection control standards. It bridges the gap between classroom learning and clinical practice‚ making it an indispensable part of a dental assistant’s education and career development.
Certifications for Dental Assistants
Certifications for dental assistants‚ such as CDA‚ enhance professionalism and skills‚ ensuring expertise in patient care‚ safety‚ and clinical procedures‚ boosting career prospects and industry credibility.
3.1 Certified Dental Assistant (CDA) Certification
The Certified Dental Assistant (CDA) certification is a prestigious credential that validates a dental assistant’s expertise in clinical and administrative skills; Offered by the Dental Assisting National Board (DANB)‚ this certification requires passing a rigorous exam that covers infection control‚ patient safety‚ and radiology procedures. To qualify‚ candidates must complete an accredited dental assisting program or have equivalent work experience. The CDA certification demonstrates a commitment to professionalism and is often required by employers to ensure high standards of patient care. It also enhances career opportunities and earning potential‚ making it a valuable investment for aspiring dental assistants.
3.2 Specialized Certifications and Their Benefits
Beyond the CDA‚ specialized certifications like Certified Preventive Functions Dental Assistant (CPFDA) and Certified Restorative Functions Dental Assistant (CRFDA) offer focused expertise. These certifications demonstrate advanced skills in areas such as pediatric dentistry‚ orthodontics‚ or oral surgery. They enhance job prospects‚ allow dental assistants to take on additional responsibilities‚ and often lead to higher salaries. Specialized certifications also signal a commitment to continuous learning and excellence‚ making dental assistants more valuable to their employers and patients. Pursuing these certifications can open doors to specialized roles and contribute to long-term career growth in the dental field.
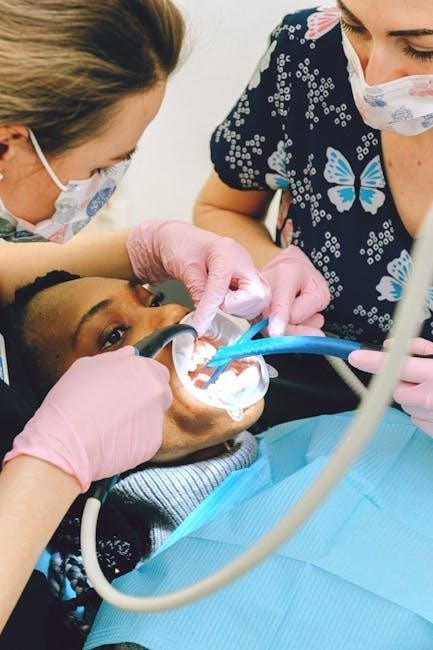
Clinical Skills and Procedures
Dental assistants must master essential clinical skills‚ including patient preparation‚ infection control‚ and assisting during procedures. Proficiency in these areas ensures safe‚ efficient‚ and high-quality patient care delivery.
4.1 Patient Preparation and Safety Protocols
Dental assistants play a vital role in preparing patients for procedures‚ ensuring their safety and comfort. This includes reviewing medical histories‚ explaining treatment plans‚ and positioning patients correctly. Proper sterilization of instruments and use of personal protective equipment (PPE) are essential to maintain infection control. Additionally‚ dental assistants must monitor patient vital signs and be prepared to handle emergencies. Clear communication and reassurance help reduce patient anxiety‚ creating a positive experience. By adhering to safety protocols‚ dental assistants contribute to efficient and successful treatments‚ upholding high standards of care.
4.2 Infection Control and Sterilization Techniques
Dental assistants must strictly adhere to infection control and sterilization protocols to ensure patient and staff safety. This involves properly sterilizing instruments using autoclaves‚ following hand hygiene practices‚ and wearing personal protective equipment (PPE). Surface disinfection and maintaining a clean environment are critical to prevent cross-contamination. Understanding proper techniques for handling biohazardous materials and waste disposal is also essential. By following established guidelines‚ dental assistants play a key role in minimizing the risk of infection transmission‚ ensuring a safe and hygienic dental care setting for all patients.
4.3 Common Dental Procedures and Assistant’s Role
Dental assistants support various procedures‚ from routine cleanings to complex surgeries. During fillings‚ they suction saliva and pass instruments to the dentist. For extractions‚ they prepare the site and ensure patient comfort. In crown placements‚ assistants handle impressions and temporary crowns. They also aid in root canals‚ orthodontic adjustments‚ and dental implants. Each procedure requires precise coordination‚ ensuring efficient workflow. Assistants prepare patients‚ maintain hygiene‚ and provide post-procedure care instructions. Their role is vital for the success of dental treatments‚ enabling dentists to focus on precision and patient outcomes while ensuring a smooth experience for everyone involved.
Administrative Duties in Dental Offices
Dental assistants handle scheduling appointments‚ managing patient records‚ and billing. They also process insurance claims‚ maintain office supplies‚ and ensure smooth communication between patients and staff members daily.
5.1 Scheduling Appointments and Managing Records
Scheduling appointments and managing records are key administrative tasks for dental assistants. They use dental management software to organize patient schedules‚ ensuring timely appointments and reducing wait times. Accurate record-keeping involves updating patient histories‚ treatment plans‚ and billing information. Dental assistants also handle cancellations and rescheduling‚ maintaining clear communication with patients. Proper management of records ensures confidentiality and compliance with regulations. This role requires strong organizational skills and attention to detail to keep the dental office running efficiently and improve patient satisfaction.
5.2 Billing and Insurance Processing
Dental assistants handle billing and insurance processing to ensure smooth financial operations. They prepare and submit claims to insurance companies‚ verifying coverage and benefits. Managing patient payments‚ including copays and deductibles‚ is a key responsibility. Assisting with insurance verification and resolving billing discrepancies helps maintain patient trust. They also update financial records and ensure compliance with billing regulations. Effective communication with patients and providers is essential to clarify billing details. Proficiency in dental billing software and understanding of insurance protocols are critical skills for efficient financial management in a dental office setting.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills
Effective communication is vital for dental assistants to ensure clear interactions with patients and team members. Strong interpersonal skills foster trust‚ collaboration‚ and a positive dental office environment.
6.1 Patient Communication and Education
Effective patient communication is essential for dental assistants to ensure patients understand their treatment plans and feel at ease. Clear‚ empathetic dialogue helps build trust and reduces anxiety. Dental assistants should use simple‚ non-technical language to explain procedures‚ address concerns‚ and provide post-care instructions. Active listening and patience are key to understanding patient needs. Additionally‚ educating patients on oral hygiene practices and preventive care fosters better health outcomes. Strong communication skills also facilitate accurate diagnosis and treatment‚ as patients are more likely to share relevant information. This role in patient education underscores the importance of clear and compassionate interaction in dental care settings.
6.2 Team Collaboration and Professionalism
Team collaboration and professionalism are vital for dental assistants to maintain a cohesive and efficient work environment. Assisting dentists and hygienists‚ dental assistants must communicate clearly and work seamlessly as part of the healthcare team. Reliability‚ respect‚ and a positive attitude foster strong working relationships. Professionalism extends to patient interactions‚ ensuring a welcoming and trustworthy atmosphere. Active participation in team meetings and continuous improvement efforts demonstrates commitment to the practice’s success. By upholding ethical standards and staying organized‚ dental assistants contribute to a harmonious and productive workplace‚ enhancing overall patient care and office efficiency.

Job Market and Career Outlook
The dental assistant job market is thriving‚ with a 5% growth rate expected through 2030. Salary expectations vary by location and experience‚ averaging $42‚000 annually. Increased demand for dental care drives this growth‚ offering promising opportunities for aspiring dental assistants.
7.1 Current Trends in Dental Assisting
Current trends in dental assisting highlight advancements in technology‚ patient-centered care‚ and specialized roles. Digital radiography and CAD/CAM systems are transforming clinical procedures‚ improving efficiency. Increased focus on preventive care and patient education is reshaping the assistant’s role. Certifications in specialized areas‚ such as orthodontics or sedation dentistry‚ are becoming more sought after. Additionally‚ the demand for bilingual assistants is rising to accommodate diverse patient populations. The integration of dental assistants into multidisciplinary healthcare teams underscores their growing importance in modern dentistry. These trends emphasize the need for continuous learning and adaptability in the field.
7.2 Growth Prospects and Salary Expectations
The dental assisting field is experiencing strong growth‚ with a projected increase in demand due to an aging population and greater emphasis on oral health. According to recent data‚ dental assistants can expect a median salary range of $38‚000 to $58‚000 annually‚ depending on experience and location. Urban areas and specialized practices often offer higher pay. Additionally‚ assistants with certifications in advanced procedures‚ such as sedation or orthodontics‚ may earn premium wages. This career path provides stability‚ competitive compensation‚ and opportunities for advancement‚ making it an attractive choice for those entering the healthcare industry.

Study Tips and Test Preparation
Effective learning strategies include creating flashcards‚ practicing with mock tests‚ and maintaining an organized study schedule. Utilize recommended resources and focus on understanding key concepts thoroughly.
8.1 Effective Learning Strategies for Dental Assistant Students
Effective learning strategies for dental assistant students involve active recall‚ spaced repetition‚ and practice tests. Organize study materials into manageable sections and review consistently. Utilize flashcards to memorize key terms and procedures. Engage in hands-on practice to reinforce clinical skills. Collaborate with peers for group study sessions to discuss challenging topics. Prioritize understanding over rote memorization‚ focusing on concepts rather than just details. Incorporate visual aids like diagrams and videos to enhance comprehension. Set specific goals for each study session and track progress. Stay organized by maintaining a dedicated study schedule and resource list.
8.2 Recommended Resources and Study Materials
For dental assistant students‚ essential study materials include textbooks like Modern Dental Assisting and Dental Assisting Notes. Online platforms such as Khan Academy and Coursera offer supplementary courses. Utilize practice exams from the Certified Dental Assistant (CDA) certification guide to prepare for licensing. Flashcards and study guides from organizations like the American Dental Assistants Association (ADAA) are also valuable. Additionally‚ subscribe to dental journals and websites for updated clinical procedures. Hands-on training tools‚ such as dental simulation software‚ can enhance practical skills. Always refer to CODA-accredited program materials for accurate and relevant content.

No Responses